
Use the lsblk command to confirm creation of the partition: $ lsblkĤ. The operation has completed successfully. OK writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/xvdh.
LINUX LOGICAL VOLUME MANAGER CODE
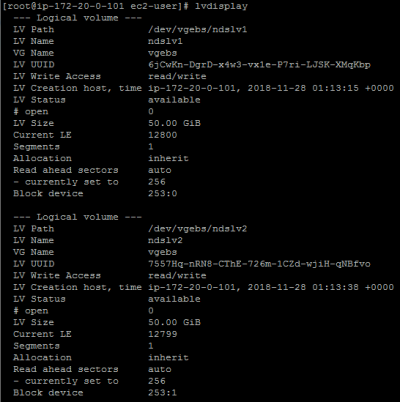
Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): 8e00 The following example creates the partition /dev/xvdh1 on /dev/xvdh. For the variable Hex code or GUID, enter 8e00. Use the gdisk command to create a partition. Create your EBS volume and then attach the volume to your instance.ģ. Open the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) console.Ģ. For more information on device naming, see Device names on Linux instances.ġ. If you're using a Nitro-based instance, then replace the device names in the following steps with the appropriate device name. The block device names follow the pattern /dev/nvme1n1, /dev/nvme2n1, /dev/nvme3n1, and so on. Note: Nitro-based instances expose volumes as NVMe devices. The underlying physical storage unit of an LVM logical volume is a block device, such as a partition of an EBS volume or an entire EBS volume. Create physical volumes on the partition of your EBS volume Note: If you already created LVM on your volume and mounted it for use, then follow the instructions beginning at Extend the logical volume. Create a logical volume (LV), and then mount the directory on the LVM.Create a volume group (VG), and then add the physical volumes into the volume group.Create physical volumes (PV) from your EBS volume.To use LVM on your EBS volume and extend the partitions, follow these steps: Using LVM, you can allocate an EBS volume or a set of EBS volumes to one or more physical volumes. LVM allows you to allocate disk space and strip, re-mirror, and resize logical volumes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
